Short answer
During sleep, the overall activity of the brain is reduced compared to the waking state. That does not mean that brain activity is low during the sleep cycle. Brain activity differs based on which sleep stage you find yourself in. During REM sleep, when you have your most vivid dreams, your brain activity is comparable to your waking state.
Longer answer
An active brain?
Some parts of the brain can be more active than others during specific tasks. For instance, when you process noise, the auditory cortex in your brain is active. But this does not mean that the rest of the brain is inactive or underutilized. All areas in the brain are strongly connected and form a complex system. Even for tasks that appear simple, you need the interaction of various brain areas. This cooperation between brain areas is also present when you think something over, when you daydream, and even when you sleep.
But what is brain activity and how do you measure it?
The communication between different brain areas, or between the brain and the rest of the body, all falls under brain activity. Brian cells, neurons to be specific, communicate amongst each other via electrical and chemical signals (more explanation here). There are various methods to measure brain activity, but the method used most often for sleep research is electroencephalography (EEG). With this method, electrodes are placed on the scalp in order to measure the electrical activity of brain cells. This method is used most often for sleep research in order to diagnose sleep disorders because the EEG is painless and the electrodes can be worn during sleep.
Different brain activity during wakefulness and sleep?
One of the first applications of EEG was the description of the different electrical brain activity between wakefulness and sleep. When you are awake, the brain is very active, processing all the sensory input in order to react to that information. Because of EEG, they discovered that brain activity is somewhat slower during sleep, and that brain cells show more synchronized activity than they would in a wakeful state. But they also quickly noticed that sleep is composed of differing stages, each with their own patterns of electrical waves: REM-sleep and NREM stage 1, 2 and 3. These stages each last 1,5-2 hours and alternate a couple of times during sleep, in a specific pattern.

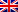
Here you see a typical sleep pattern from the moment you fall asleep (left) to the moment you wake up in the morning. Source: Elena Krugliakova.
Different sleep stages?
The “REM” in REM-sleep means Rapid Eye Movement. This is due to the fact you can recognize this sleep stage from the visible rapid, short movements of the eyes under the eyelid. As opposed to the rapid eye movement, the rest of the body has absolutely no muscle tension whatsoever during REM sleep: you are temporarily paralyzed. In general, REM sleep is marked by high brain activity, especially in areas involved with emotional processing, memories and visual and motor functions. This brain activity is similar to the awakened state. During REM sleep you have your most vivid and longest dreams.
During NREM (“Non-Rapid Eye Movement”) sleep, your eyes usually do not move but the rest of your body can move a bit. You can dream, but it occurs less often than during REM sleep. During NREM stage 1, your sleep is light, it is deeper in stage 2 and stage 3 is truly deep sleep. When you are woken up during this deep sleep, you often feel disoriented. During NREM sleep, your brain is active but in a different way to a wakeful state. The brain cell activity is slower and the cells often fire their electrical signals simultaneously. Your brain activity is slowest during deep sleep. NREM sleep is very important for the clearing and expelling of waste products from your brain cells and the consolidation of your memories (read more about the formation of memories here). While the brain shows less activity than when it is awake, you do see specific brain activity patterns during sleep, and the activity present in REM sleep is very similar to a wakeful state.