Short answer
Yes.
Longer answer
MRI scanners create images by harnessing the electrical charge found in the brain – and in all matter – specifically in water molecules. Water consists of three atoms (two hydrogen atoms, ‘H’, shown in white below, and one oxygen atom, ‘O’, shown in red below, together forming H₂O). Each atom is made up of different components: positively charged protons, negatively charged electrons, and uncharged neutrons. The signal an MRI scanner measures comes from the hydrogen atoms’ protons.
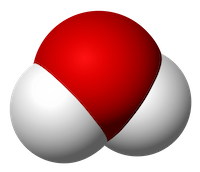
Image: A water molecule with two hydrogen atoms (white, ‘H’) and one oxygen atom (red, ‘O’). Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Water
The image generated by the MRI scanner
The signals detected by an MRI scanner are electromagnetic waves, similar to radio waves or light. These signals originate from water molecules and have a specific frequency. To create an image, the area being scanned is placed inside a strong (main) magnet. This magnetic field is then made to oscillate at a precise frequency that excites the protons in the water molecules. These protons respond by emitting electromagnetic signals (similar in frequency to radio waves), which are picked up by coils. Coils are loops of conductive wire, and when a changing magnetic field passes through them, they generate a measurable electric current (see this Wikipedia page on coils).
The noise generated by the MRI scanner
When the coils are activated to produce an image, electric currents flow through the wires of the coils. In the presence of a magnetic field, these currents generate a force known as the Lorentz force. Since the coils are inside the magnetic field of the main magnet, they experience this force, causing them to deform slightly. The rapid changes in the magnetic field create repeated strong forces on the coils, making them vibrate and producing the characteristic noise of an MRI scanner. The stronger the magnetic field, the greater the forces on the coils and, consequently, the louder the noise.
Why use a 14T MRI scanner?
A stronger magnetic field allows for more precise imaging. A 14T MRI scanner can produce significantly higher-resolution images than a 3T scanner, making it ideal for detailed studies, such as of the brain.

Image: A brain scan captured using an MRI scanner.